Blockchain anti-corruption is increasingly viewed as a structural reform rather than a technical experiment. Corruption drains nearly $3 trillion each year from the global economy. As a result, growth weakens across both developed and developing regions. Moreover, public trust erodes when institutions fail to protect public resources.
Traditional governance tools remain dominant. However, they depend heavily on delayed audits and manual oversight. Consequently, corruption is often detected only after damage occurs. This reactive approach limits deterrence and weakens accountability.
Blockchain-based anti-corruption systems alters this framework. It embeds transparency directly into transactions and records. Therefore, manipulation becomes visible in real time. In addition, immutable ledgers reduce opportunities for discretion. This shift strengthens governance in procurement, finance, and service delivery.
Introduction
Blockchain-based anti-corruption systems has emerged as a response to persistent institutional failure. Each year, corruption diverts resources from development priorities. Consequently, public services suffer. At the same time, fiscal pressures intensify.
Corruption thrives in opaque systems. Moreover, fragmented oversight allows informal power to dominate decision-making. As a result, enforcement mechanisms lose credibility. blockchain-enabled accountability systems offers a structural alternative by securing records, timestamping decisions, and enabling continuous auditability.
The World Bank emphasizes that digital transparency tools improve public financial management and reduce misuse of public resources https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/governance
The Economic Cost of Corruption
Corruption imposes costs far beyond direct financial theft. It distorts markets and discourages long-term investment. Furthermore, it weakens confidence in institutions. Transparency International consistently shows that economies with weak transparency face deeper economic losses https://www.transparency.org/en/cpi

Government procurement absorbs the largest share of corruption losses. Therefore, Blockchain-based anti-corruption systems is most effective when applied to spending, contracting, and payment systems. Moreover, traceable procurement reduces discretion and strengthens audit trails. The World Economic Forum highlights blockchain’s role in improving oversight and accountability https://www.weforum.org/stories/2020/07/5-ways-blockchain-could-help-tackle-government-corruption/
Blockchain-based anti-corruption systems in High-Risk and Fragile Economies
Fragile economies experience corruption losses that are large relative to GDP. Consequently, development outcomes weaken rapidly. In addition, public trust declines.
In Pakistan, corruption-related governance failures have intensified poverty, fiscal stress, and service delivery gaps, particularly at the provincial level, as documented in the analysis of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa’s economic crisis https://economiclens.org/kp-economic-crisis-poverty-corruption-pressures-and-financial-strain/

Losses remain severe relative to economic size. As a result, fiscal collapse accelerates. blockchain-enabled accountability systems improves traceability in such environments. Therefore, leakages decline and accountability improves.
Blockchain Anti-Corruption, Growth, and Inequality
Corruption directly suppresses growth. Moreover, it widens inequality by diverting resources away from vulnerable groups. Consequently, human development outcomes deteriorate.
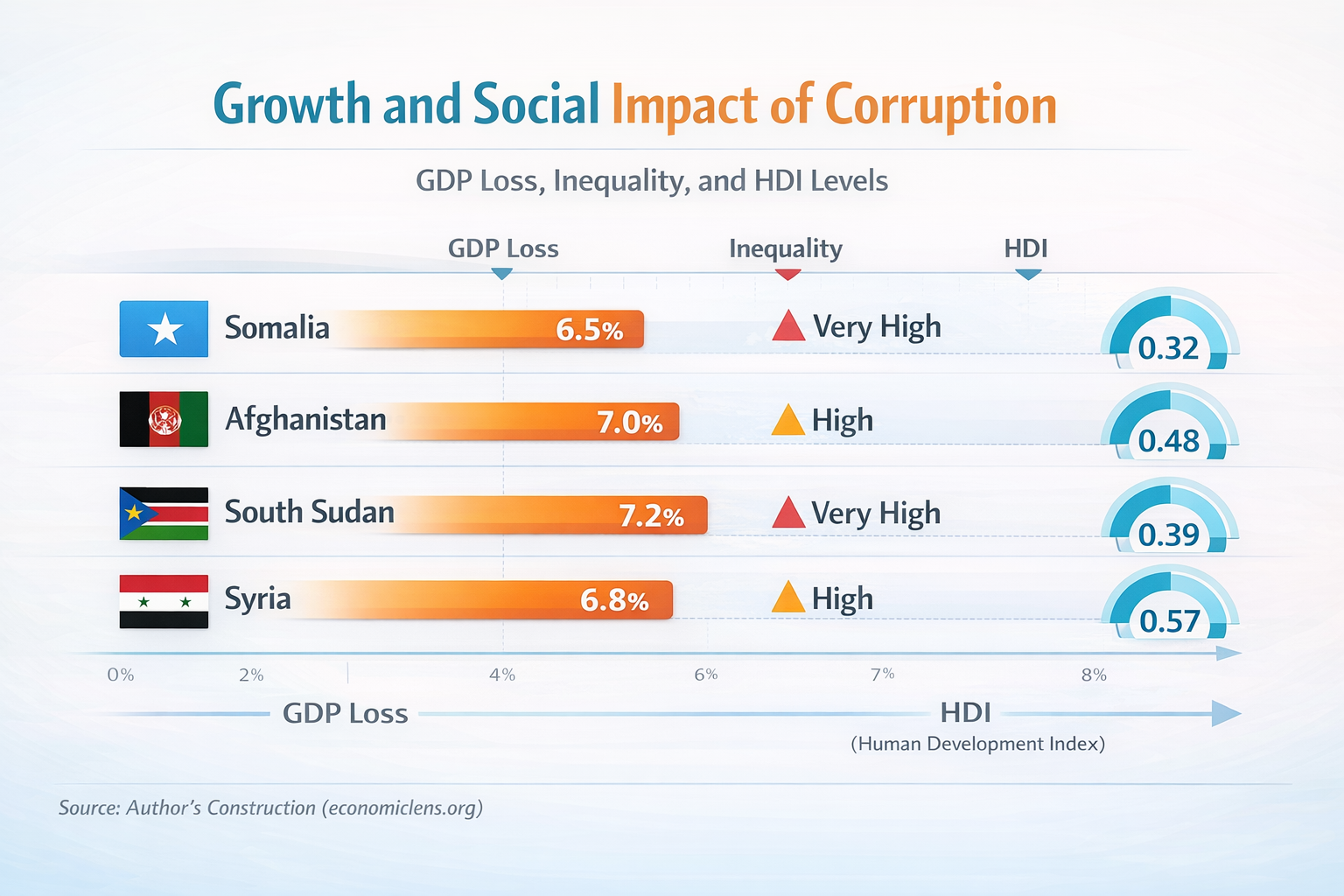
Lower growth and rising inequality reinforce each other. Therefore, Blockchain-based anti-corruption systems becomes a long-term development reform rather than a narrow compliance tool.
From Traditional Controls to Blockchain-based anti-corruption systems
Traditional anti-corruption tools rely on delayed audits and investigations. Consequently, losses often go undetected. Blockchain-based systems operate continuously and reduce reliance on manual oversight.
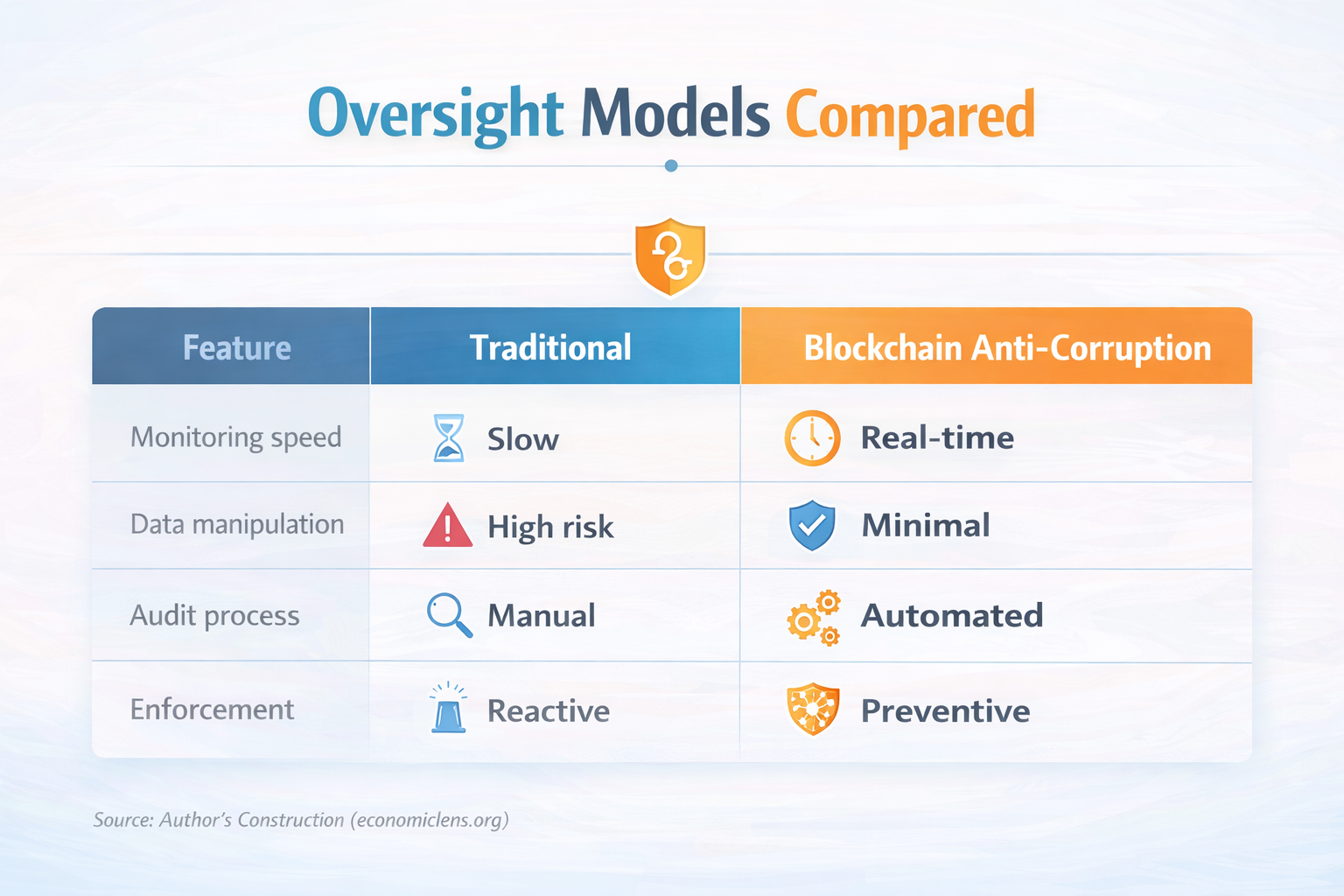
blockchain-enabled accountability systems shifts governance incentives. Misconduct becomes visible immediately. Therefore, prevention replaces reaction. The World Bank highlights this shift in digital governance reforms https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/governance/brief/anti-corruption
Key Technologies Supporting Blockchain-based anti-corruption systems
Blockchain functions most effectively when combined with complementary tools. Together, they strengthen transparency and detection capacity.
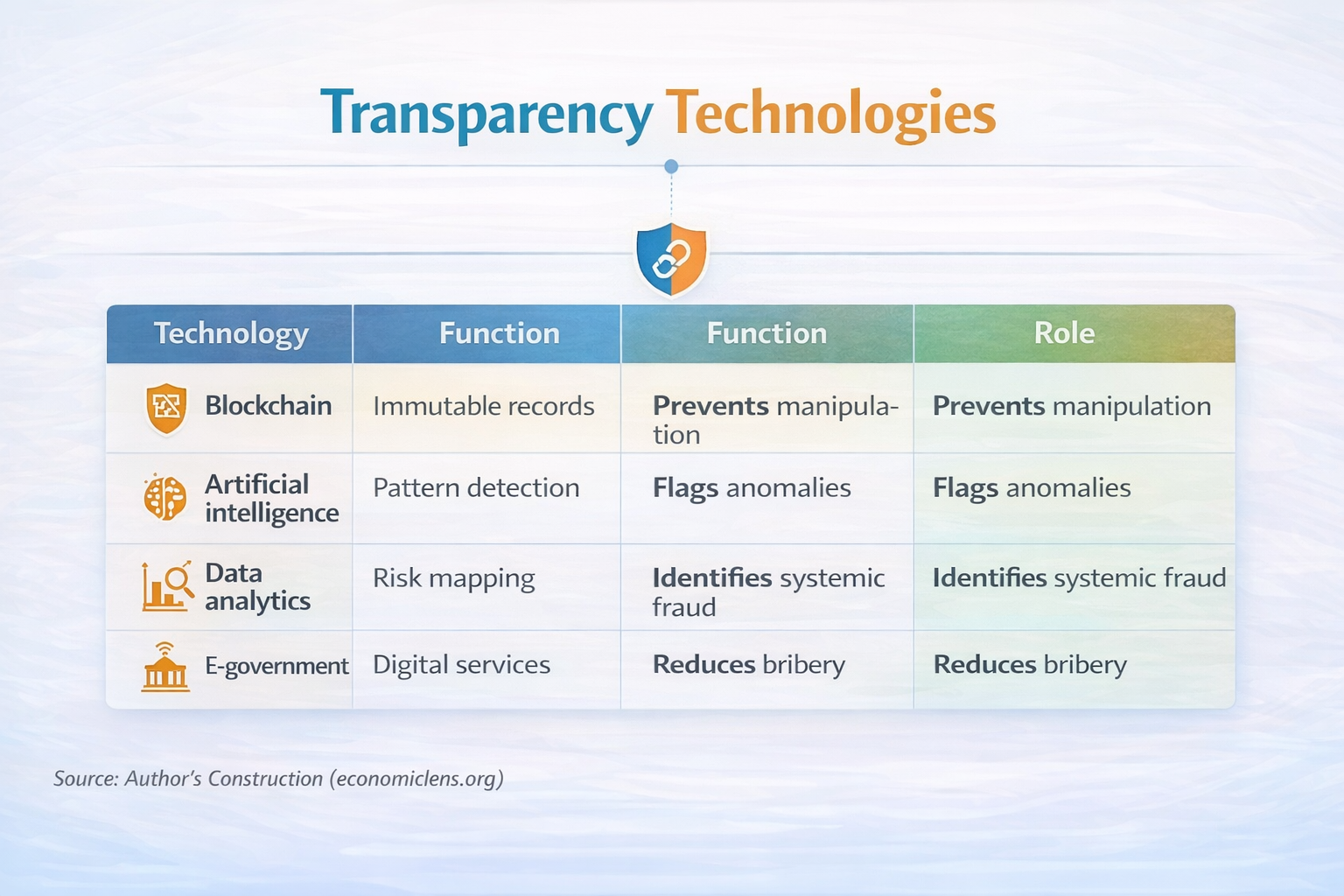
AI enhances early detection, while analytics reveal risk patterns. Transparency International confirms that digital tools significantly strengthen accountability when integrated effectively https://knowledgehub.transparency.org/helpdesk/harnessing-artificial-intelligence-ai-for-anti-corruption
Digital Governance Transparency Using Blockchain in Practice
Several countries demonstrate measurable governance improvements through digital transparency. Adoption delivers results when systems scale nationally.

Ukraine’s Prozorro platform further demonstrates how digital procurement improves transparency and competition in public contracts https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Prozorro
Policy Design and Institutional Reform
Technology alone cannot eliminate corruption. Policy alignment remains critical. Informal influence and political interference often undermine reform.
This dynamic is visible in Pakistan’s governance debates, where political authority frequently overrides institutional discipline https://economiclens.org/bushra-bibis-influence-pti-governance-comparing-the-economists-claims-with-pakistans-economic-reality/
State-owned enterprises illustrate these risks clearly. Pakistan’s airline privatization experience shows how opacity distorts reform outcomes https://economiclens.org/pia-privatization-crisis-behind-pakistans-airline-sale/
Key priorities include:
- Public-private partnerships
- Clear regulatory frameworks
- Institutional capacity building
Without coordination, transparency technology remains fragmented.
Conclusion: Making Blockchain-based anti-corruption systems Structural
Blockchain anti-corruption transforms governance design. It shifts accountability from discretion to structure. As a result, corruption becomes harder to execute.
The $3 trillion corruption burden demands prevention rather than reaction. Therefore, transparency technology must scale across institutions. When supported by policy reform, blockchain-enabled accountability systems embeds integrity into daily governance.
Corruption thrives in opacity. Transparency changes that permanently.






2 thoughts on “Blockchain Anti-Corruption: Can Transparency Technology Cut the $3 Trillion Cost?”
Hello! Someone in my Facebook group shared this site with us so I came to look it over. I’m definitely loving the information. I’m bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Wonderful blog and brilliant design and style.
We would also like to state that most individuals that find themselves without health insurance are generally students, self-employed and those that are laid-off. More than half of the uninsured are really under the age of Thirty-five. They do not feel they are requiring health insurance because they are young and also healthy. The income is typically spent on real estate, food, and also entertainment. A lot of people that do represent the working class either full or as a hobby are not made available insurance by means of their work so they go without owing to the rising expense of health insurance in the us. Thanks for the tips you talk about through this website.