Ocean acidification is jeopardizing marine ecosystems and global food security. As CO2 levels rise, ocean acidity increases, threatening marine life, fisheries, and the seafood supply chain. This blog explores the causes, effects, and potential solutions to combat ocean acidification and secure the future of both ocean health and global food security.
Introduction
Oceans are the lifeblood of our planet, providing vital resources that support global food security. However, ocean acidification—the gradual acidification of ocean waters due to excess carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere—is now threatening the balance of marine ecosystems and global food security. This shift in ocean chemistry poses serious risks to marine life, disrupts food chains, and jeopardizes the future of seafood-based nutrition for billions of people. In this blog, we will explore ocean acidification’s impact on food security, and the urgent need for global action.
“The time to act is now. Our oceans need protection, and every step we take today will determine the health of our oceans—and the future of food security.”
1. Understanding Ocean Acidification and Global Food Security
Ocean acidification occurs when excess CO2 from the atmosphere is absorbed by the oceans, reacting with water to form carbonic acid, which lowers ocean pH levels. This subtle, yet continuous, change is gradually disrupting marine ecosystems and threatening species that rely on calcium carbonate to form shells and skeletons, such as shellfish, corals, and plankton. These species are vital for global food security, as they form the base of the marine food chain.
Dr. Jane Thompson, Marine Biologist at the Oceanic Research Institute, explains:
“Ocean acidification is a hidden crisis that’s slowly but steadily undermining the health of our oceans. As carbon dioxide levels increase, the acidity of the oceans is rising, which disrupts the basic chemistry of marine life. Species that rely on calcium carbonate to form shells and skeletons—like corals, mollusks, and certain plankton—are particularly vulnerable. This not only threatens marine biodiversity but also the global food security of millions of people who rely on these ecosystems.”
“While the crisis may seem gradual, our actions can have an immediate effect. We have the power to slow ocean acidification and protect the marine life that sustains billions of people.”
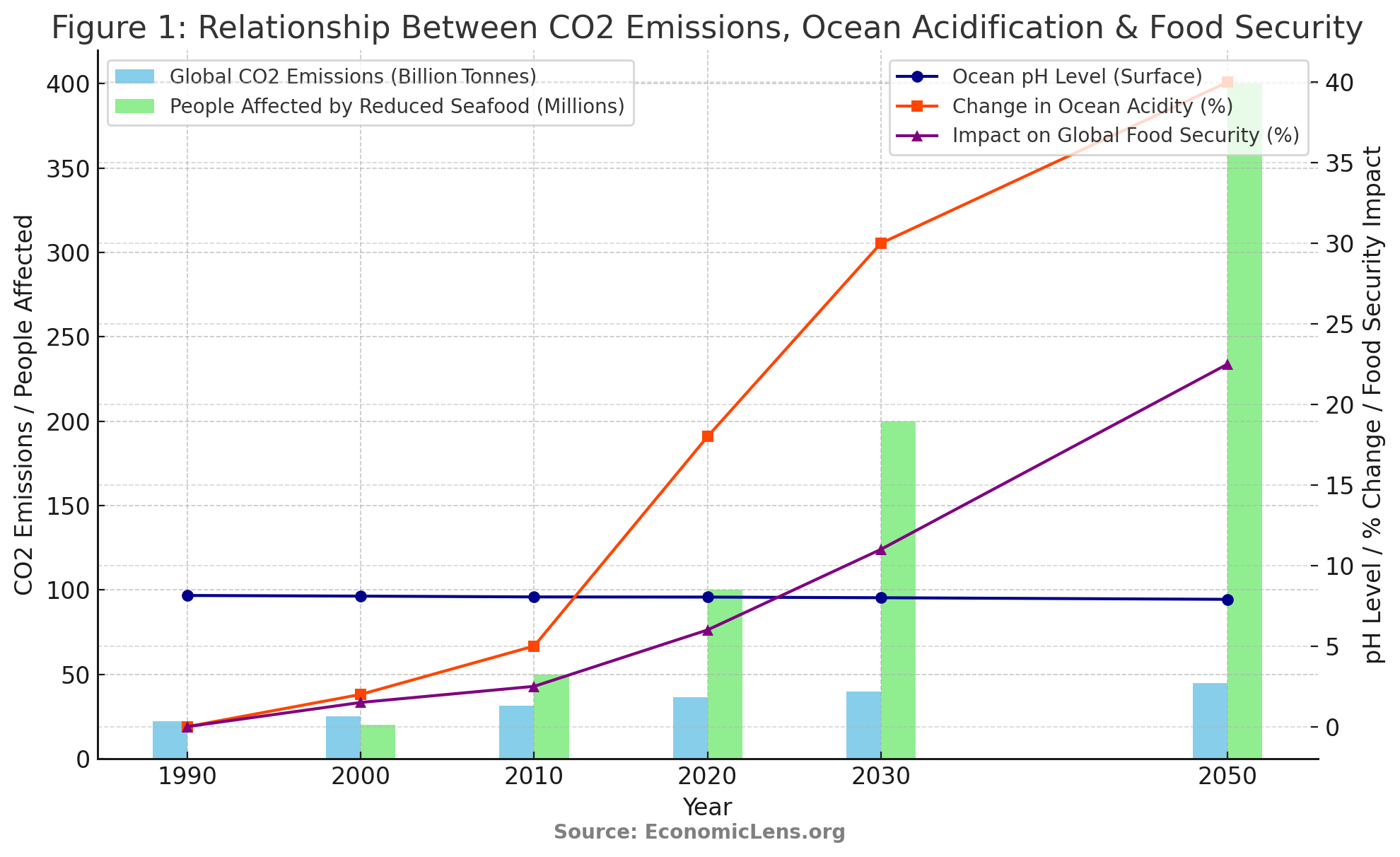
This figure outlines the relationship between rising carbon emissions, ocean acidification, and the impact on food security over time. As global CO2 emissions increase from 22.3 billion tonnes in 1990 to 45 billion tonnes by 2050, ocean pH levels steadily decrease, leading to higher acidity in the oceans. This will have severe consequences for marine species, including shellfish, coral reefs, and fish, with over 400 million people projected to be affected by seafood shortages by 2050. The data shows a direct link between carbon emissions and food security, underscoring the need for urgent action to reduce emissions.
It also unfolds that as ocean acidification progresses, the projected impact on marine species escalates, leading to a corresponding decline in global seafood supply. Initially, the impact is minimal, affecting only a small fraction of shellfish and fish populations. However, as acidity increases, we see a moderate impact on plankton and fish, causing a moderate decline in seafood supply. In the coming decades, the impact intensifies, significantly affecting shellfish, corals, and fish, leading to a major decrease in fisheries production. By mid-century, the damage will become severe, causing a substantial decline in seafood availability. Ultimately, the collapse of marine food chains could result in major shortages in global seafood supply, threatening food security for millions.
“This is a wake-up call. The data is clear—we must take action now to reduce CO2 emissions and protect marine ecosystems for the future of our food supply.”
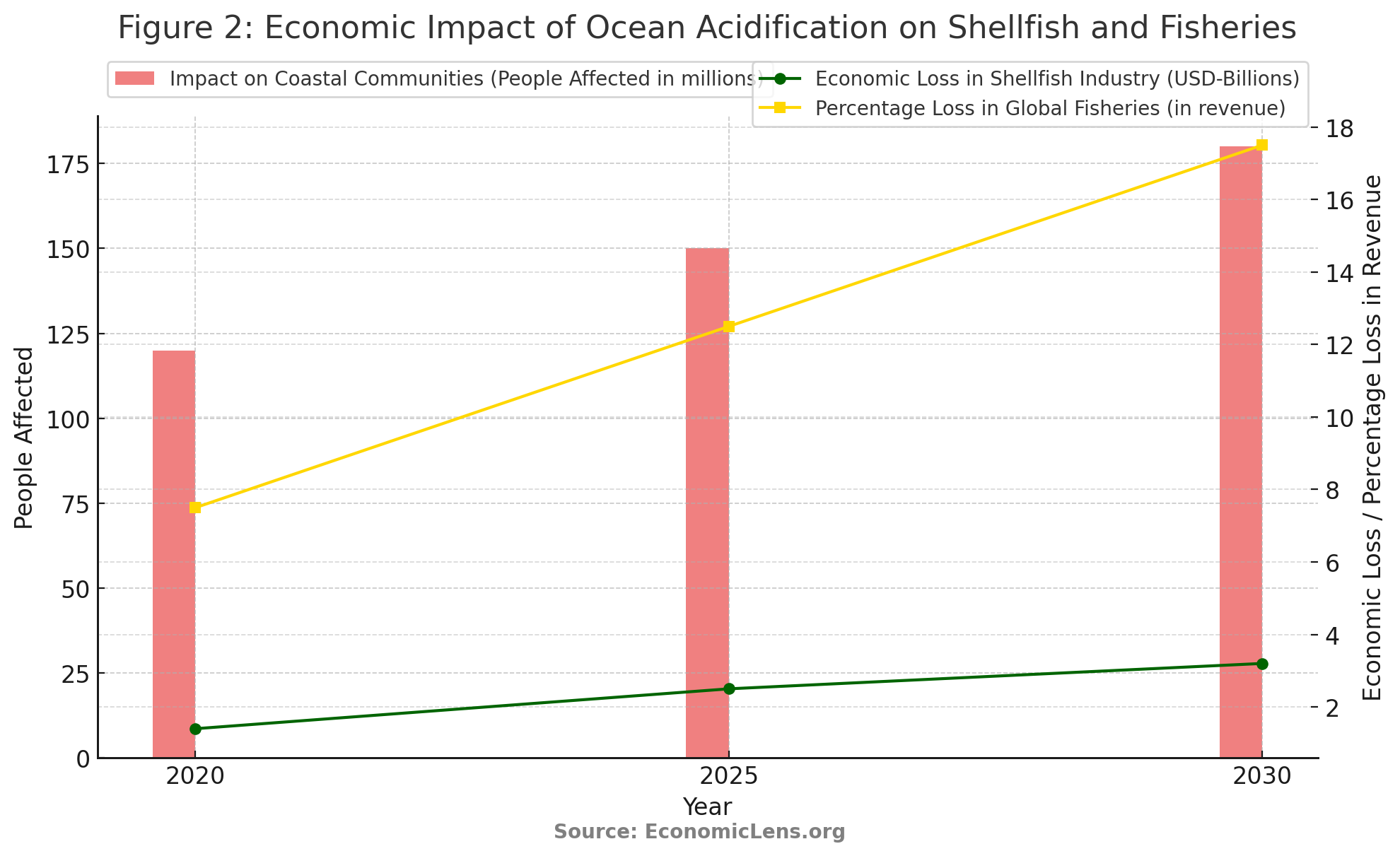
This figure highlights the economic impact of ocean acidification on shellfish and global fisheries. The $3.2 billion loss projected for 2030 underlines the growing threat to coastal industries and the livelihoods of millions of people. Acidification impacts shellfish production—a key food source for coastal communities—and disrupts the overall fisheries sector, which is vital for global food security. The data clearly shows the urgent need for action to mitigate ocean acidification and protect coastal communities and industries.
“The numbers may be alarming, but with decisive action, we can prevent these losses and secure a future where marine industries thrive alongside healthy ecosystems.”
2. The Impact of Ocean Acidification on Marine Life
As ocean acidity increases, species that rely on calcium carbonate to form their shells and skeletons—like shellfish, corals, and plankton—are struggling to survive. These species are crucial to marine food webs, and their decline can have cascading effects, threatening the stability of marine ecosystems and the food security of billions. The impacts of ocean acidification are particularly severe in regions heavily dependent on fisheries and aquaculture.
A recent study published by the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) notes:
“Marine ecosystems are integral to the health of our planet and human food security. The impact of ocean acidification is profound, especially for species like corals, shellfish, and plankton. These species form the foundation of marine food chains and are essential to food security in coastal populations. As acidification progresses, the ability of these species to thrive decreases, leading to a cascade of negative effects throughout the marine food web.”
“While the effects are clear, there’s hope. By acting now to reduce emissions and protect marine ecosystems, we can prevent further damage and safeguard the food systems that billions rely on.”
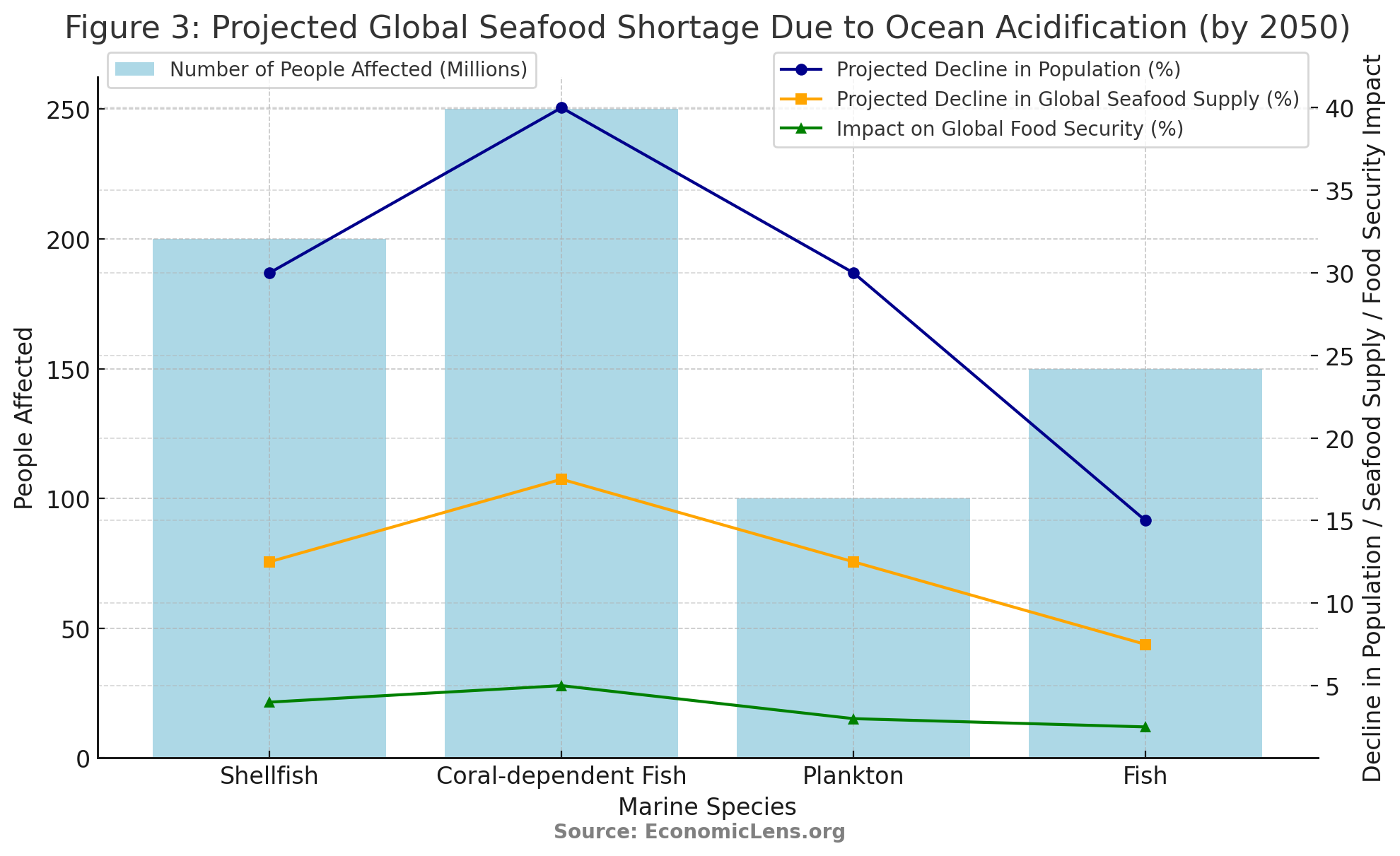
This figure illustrates the projected decline in seafood supply due to ocean acidification. The 25-40% decline in shellfish populations and the 30-50% decline in coral-dependent fish by 2050 could lead to a severe seafood shortage, affecting over 200 million people globally. The decline in plankton—the foundation of the marine food web—will have significant ripple effects, potentially leading to global food security risks. As the ocean becomes more acidic, millions of people who rely on seafood for protein will face a critical shortage, exacerbating global food security concerns.
“This crisis may seem daunting, but by addressing the root causes—starting with reducing CO2 emissions—we can avert the worst impacts and secure a sustainable future.”
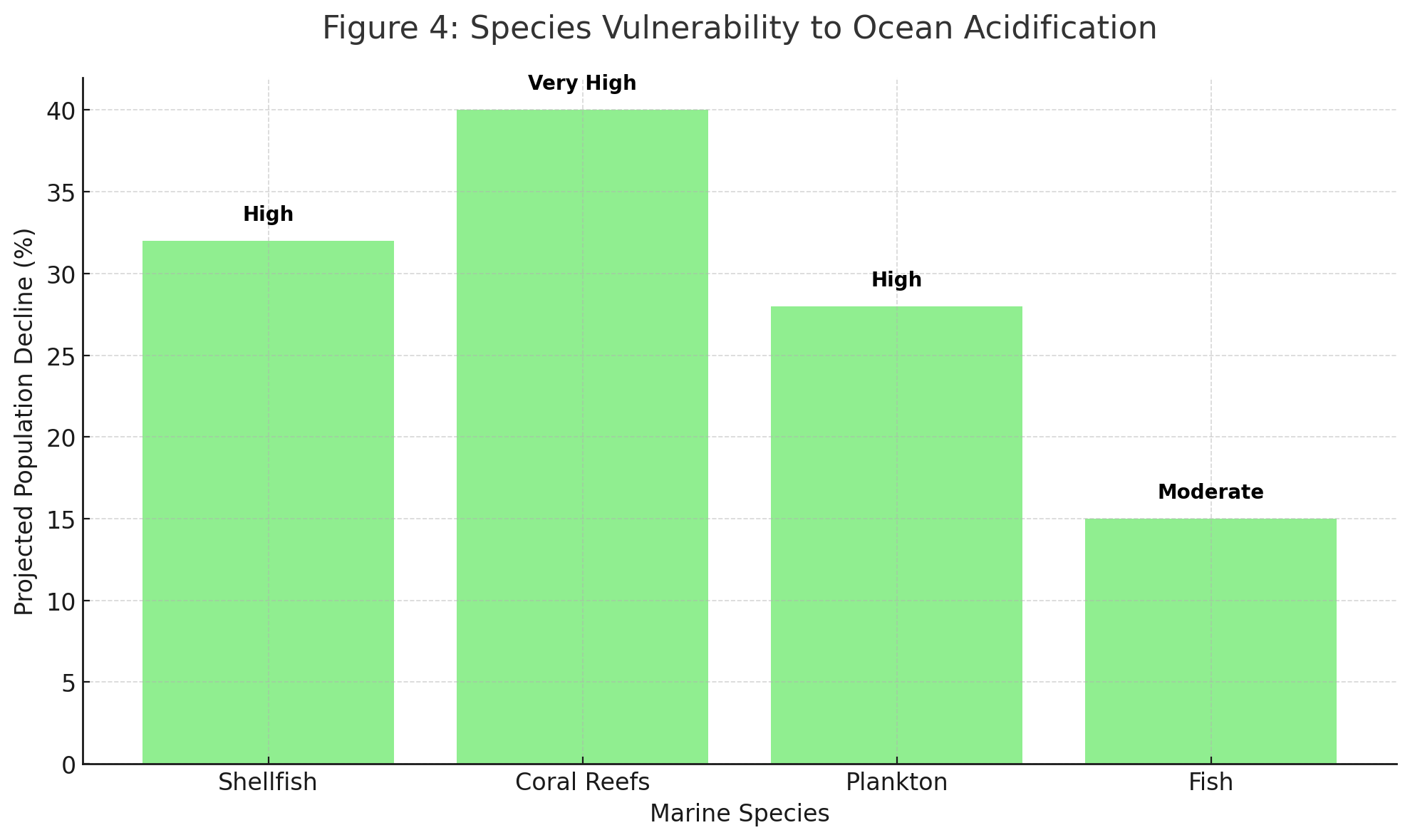
This data highlights the vulnerability of key marine species to ocean acidification. Species like shellfish and coral reefs are highly sensitive to changes in ocean pH, and their decline could have devastating effects on marine biodiversity and food security. With over 200 million people relying on shellfish as a primary food source, and coral reefs supporting over 70% of marine species, their decline will affect both fisheries and food systems. Protecting these species is crucial to preserving marine ecosystems and ensuring global food security.
Ocean acidification threatens food security, especially in coastal regions like the U.S., Europe, and Asia, where marine species like shellfish and fish are key protein sources. The disruption of the marine food web, particularly in Pacific Islands and the Caribbean, is a major concern, as it affects critical species like plankton and coral reefs. This impacts global marine biodiversity and food chains, leading to a global impact on food security. Northern Hemisphere fisheries, relying on fish stocks such as cod and haddock, face a decline in available fish, worsening both economic and nutritional security for affected populations.
“By protecting vulnerable species today, we not only preserve marine life, but also safeguard the future of global food security for generations to come.”
3. Solutions to Combat Ocean Acidification
Addressing ocean acidification requires a multi-faceted approach to reduce carbon emissions, protect marine ecosystems, and invest in sustainable practices. Solutions include transitioning to renewable energy sources, improving coastal management, and implementing carbon capture technologies. Governments, industries, and individuals must all play a role in combating this growing crisis.
Dr. Sarah Miller, Ocean Policy Expert at the Global Environmental Institute, states:
“While ocean acidification is a complex issue, the solutions are within reach. Reducing carbon emissions, protecting marine ecosystems, and investing in sustainable practices are critical steps in mitigating ocean acidification. Moreover, policies that incentivize carbon capture technologies and reduce CO2 emissions will play a crucial role in reversing the current trend.”
“The solutions are in our hands. By acting now—through policy change, innovation, and individual action—we can restore the health of our oceans and secure a stable, sustainable food supply for future generations.”
Conclusion
Ocean acidification is a growing crisis that threatens both marine life and global food security. The economic impact of declining marine species, especially shellfish and fish populations, will disrupt food systems and affect billions of people who rely on seafood for nutrition. The projections are alarming, but through collective action to reduce emissions and protect marine ecosystems, we can secure a sustainable future.
Call to Action:
We must act now. Reducing emissions, protecting marine ecosystems, and embracing sustainable practices will safeguard the oceans and our food supply for future generations.





5 thoughts on “Ocean Acidification: The Silent Crisis Threatening Global Food Security”
Economic Lens is a highly informative platform that breaks down complex economic and environmental issues in a simple and engaging way. Each article is well-researched and provides clear insights that are easy to understand. A great resource for both students and professionals.
https://economiclens.org/ocean
میں نے متعدد مضامین پڑھے، ہر مضمون اپنے موضوع پر مکمل گرفت رکھتا ہے۔ Economic Lens ایک علمی خزانہ ہے جو نئی نسل کو سیکھنے میں مدد دیتا ہے۔
ماحولیات، معیشت اور پائیداری جیسے موضوعات کو جس گہرائی سے یہاں بیان کیا گیا ہے، وہ واقعی قابلِ تعریف ہے۔ ایسے پلیٹ فارمز کی آج کے دور میں اشد ضرورت ہے۔
یہ ویب سائٹ معیاری مواد کی مثال ہے۔ یہاں ہر تحریر دلیل اور حوالوں پر مبنی ہوتی ہے، جو اسے مستند اور قیمتی بناتی ہے۔